Introduction
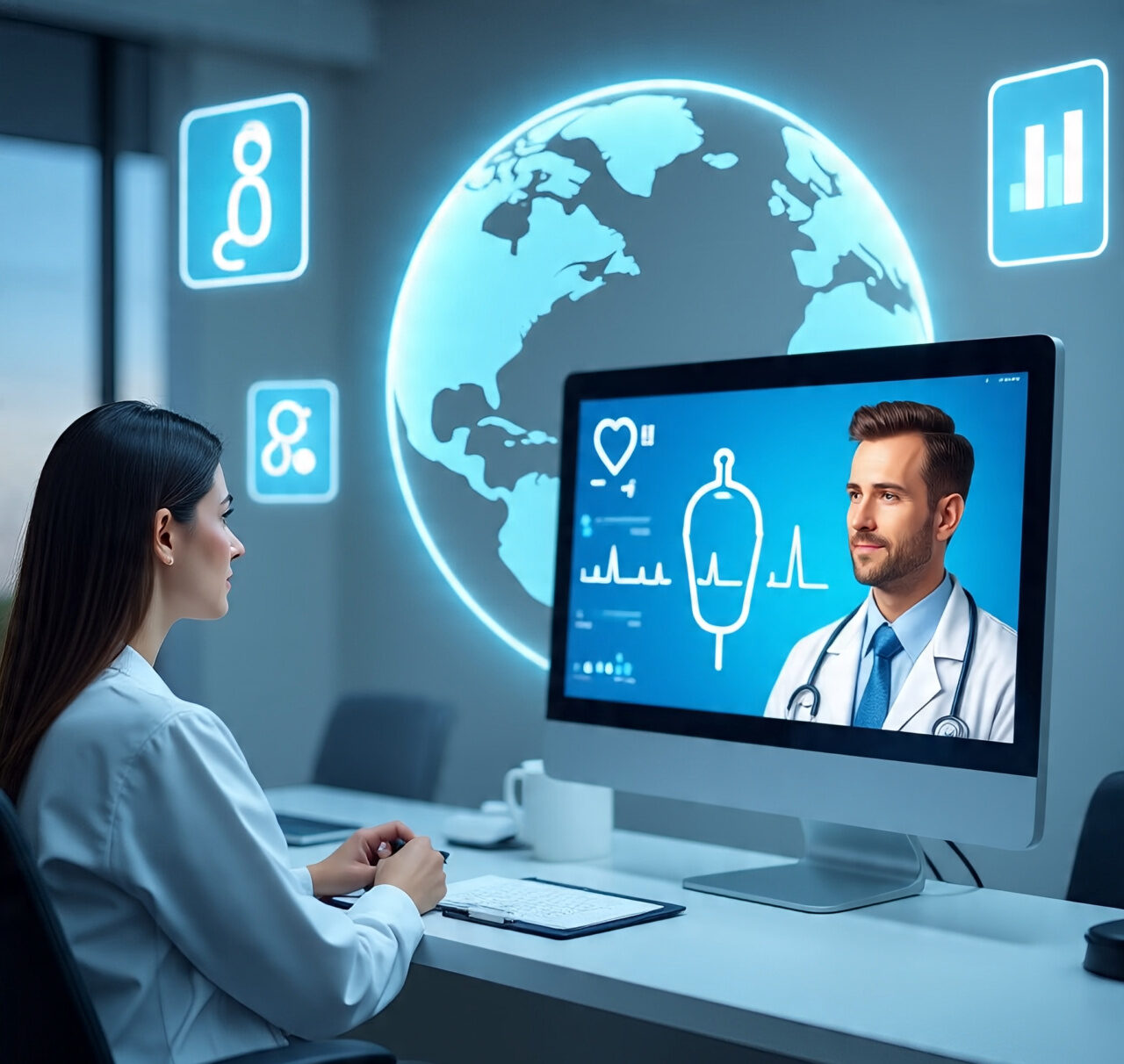
Healthcare has always faced a challenge: how to deliver quality care to people regardless of location, cost, or accessibility. For decades, patients in rural areas or developing countries have struggled to get timely medical attention. Enter telemedicine —a digital healthcare solution that is transforming the way patients connect with doctors.
Telemedicine leverages video calls, mobile apps, and remote monitoring tools to provide healthcare anytime, anywhere. By removing geographical and financial barriers, it is becoming a lifeline for millions worldwide, especially in underserved communities.
What is Telemedicine?
Telemedicine refers to the use of digital technology to provide healthcare services remotely. Instead of visiting a clinic in person, patients can consult with doctors through:
- Video calls and online consultations
- Mobile health apps for chronic disease management
- Remote monitoring devices like smartwatches and glucose trackers
- AI-powered chatbots that guide patients with basic health advice
This approach not only saves time but also makes specialist care accessible to patients who may live thousands of miles away.
Breaking Barriers in Healthcare Access
The biggest strength of telemedicine is its ability to bridge the healthcare gap between urban and rural populations, developed and developing nations.
- Geographic Barriers: Patients in remote villages can connect with top specialists in cities without traveling long distances.
- Financial Barriers: Virtual consultations often cost less than in-person visits, making healthcare more affordable.
- Time Barriers: Immediate access to doctors reduces long waiting times for appointments.
- Cultural & Language Barriers: Many telemedicine platforms offer translation tools, ensuring patients and doctors can communicate effectively.
For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic, telemedicine became a global necessity, ensuring continuity of care when hospitals were overwhelmed.
Benefits of Telemedicine for Patients and Providers
Telemedicine offers value not just for patients, but also for doctors, hospitals, and healthcare systems.
For Patients:
- Quick access to doctors without travel
- Affordable consultations
- Better management of chronic diseases
- More privacy for sensitive health issues
For Providers:
- Expanded patient reach beyond physical clinics
- Reduced hospital crowding
- Improved patient monitoring through real-time data
- More efficient use of healthcare resources
This mutual benefit makes telemedicine one of the most sustainable innovations in modern healthcare.
The Role of Technology in Telehealth
Telemedicine would not be possible without digital healthcare innovations. Key technologies driving this transformation include:
- High-speed internet & 5G: Enables smooth video consultations even in rural areas.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Assists in diagnostics, chatbots, and predictive healthcare.
- Wearables & IoT Devices: Track vital signs like blood pressure, oxygen levels, and heart rate.
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs): Allow seamless sharing of medical histories between providers.
Together, these technologies make healthcare faster, smarter, and more connected.
Telemedicine and Global Healthcare Collaboration
Telemedicine is also reshaping global healthcare collaboration. Specialists across borders can now consult on complex cases, and patients traveling abroad can share medical histories instantly with new doctors.
For example:
- A cardiologist in the U.S. can provide guidance to a rural clinic in Africa.
- A patient in India can consult an expert in Germany without leaving home.
- Researchers can use telemedicine data to track global health trends.
This level of collaboration is helping to create a truly connected healthcare ecosystem.
Challenges and the Road Ahead
Despite its benefits, telemedicine still faces some challenges:
- Digital Divide: Limited internet access in remote areas.
- Privacy Concerns: Protecting sensitive patient data from cyber threats.
- Regulations: Different countries have varying rules for telehealth services.
- Trust Issues: Some patients still prefer in-person visits.
However, with governments and healthcare organizations investing in digital infrastructure and cybersecurity, telemedicine is set to become even more reliable and accessible.

Conclusion
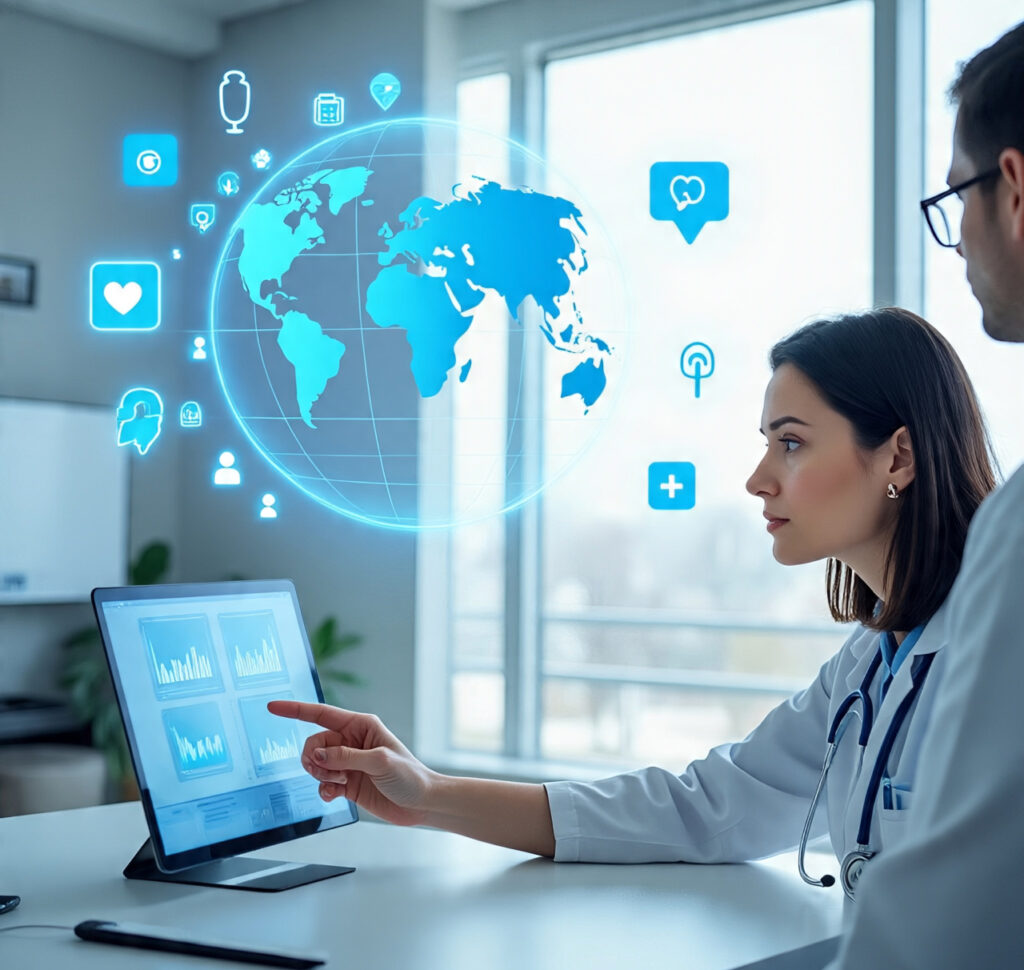
Telemedicine is no longer just a convenience—it is a revolution in global healthcare access. By breaking down barriers of distance, cost, and time, it ensures that quality medical care reaches people who once had little to no access.
As we move further into 2025 and beyond, telemedicine will continue to play a pivotal role in building a healthier, more connected world, where healthcare is not limited by geography but is accessible to all.